Epidemiology and Etiology
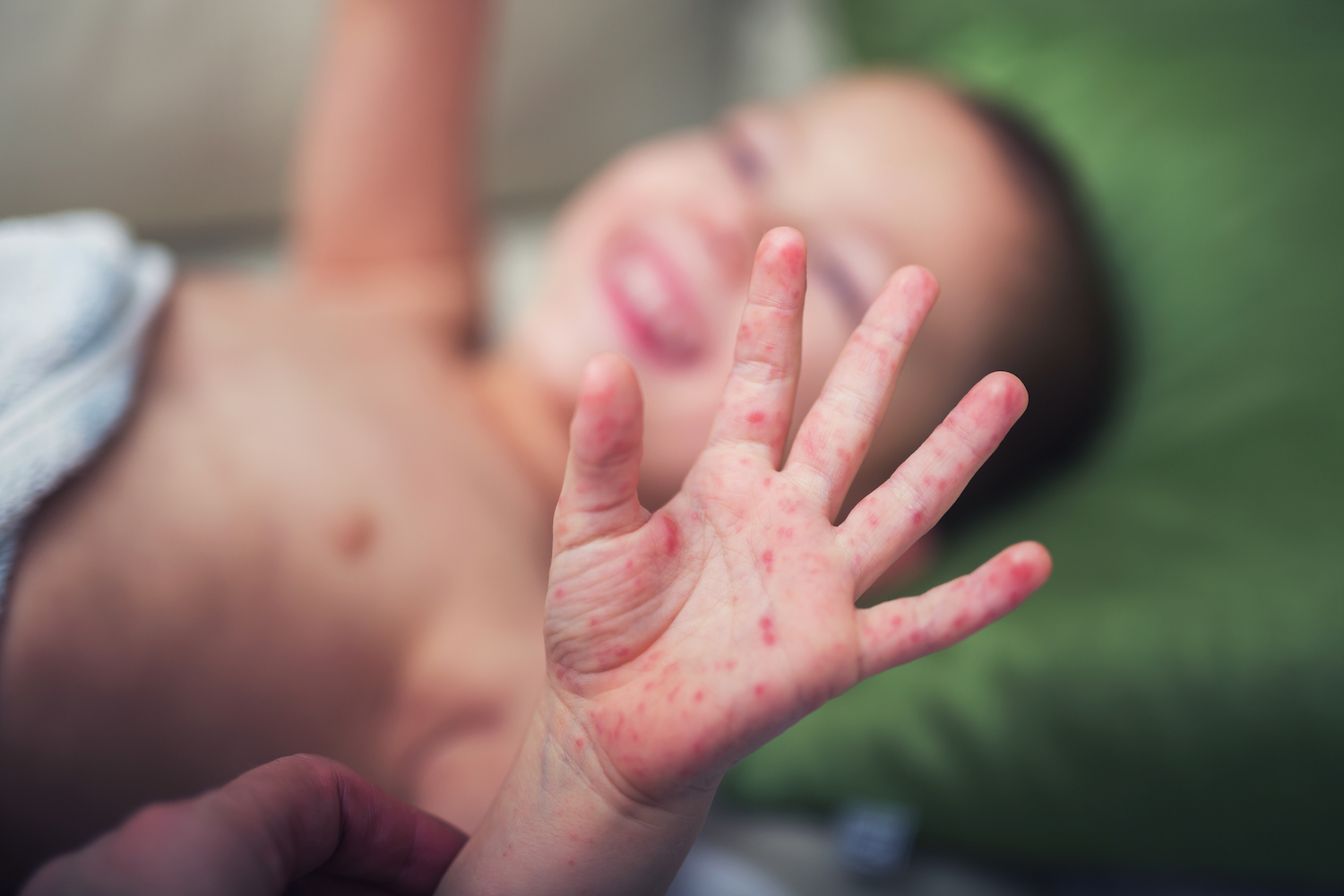

Hand foot and mouth disease – Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infectious disease caused by a virus. It is characterized by fever, sore throat, and a rash on the hands, feet, and mouth. HFMD is most commonly seen in children under the age of 5, but it can also occur in adults.
HFMD is a global problem, with outbreaks occurring in all parts of the world. The disease is most common in the summer and fall months. In the United States, there are an estimated 1 million cases of HFMD each year.
Hand foot and mouth disease is a common childhood illness that is caused by a virus. The virus is spread through contact with saliva or mucus from an infected person. Symptoms of hand foot and mouth disease include fever, sore throat, rash, and blisters on the hands, feet, and mouth.
While there is no specific treatment for hand foot and mouth disease, most people recover within a few weeks. In some cases, the virus can cause more serious complications, such as meningitis or encephalitis. Davante Adams’ parents have spoken out about the importance of early diagnosis and treatment of hand foot and mouth disease.
Etiology, Hand foot and mouth disease
HFMD is caused by a virus called the coxsackievirus. There are several different strains of the coxsackievirus, and each strain can cause different symptoms. The most common strain of the coxsackievirus that causes HFMD is called the A16 strain.
Transmission
HFMD is spread through contact with an infected person’s saliva, mucus, or feces. The virus can also be spread through contact with contaminated objects, such as toys, doorknobs, or countertops.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease, a common childhood illness, can cause fever, sores in the mouth, and a rash on the hands and feet. While not typically serious, it can be uncomfortable and contagious. In a similar vein, Davante Adams’ shoulder injury , sustained during a football game, has raised concerns about his ability to play.
Like hand, foot, and mouth disease, injuries can sideline individuals from their daily activities and require rest and recovery.
Risk Factors
Children under the age of 5 are at the highest risk of developing HFMD. Other risk factors for HFMD include:
- Close contact with an infected person
- Attending daycare or preschool
- Living in a crowded household
- Having a weakened immune system
Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis
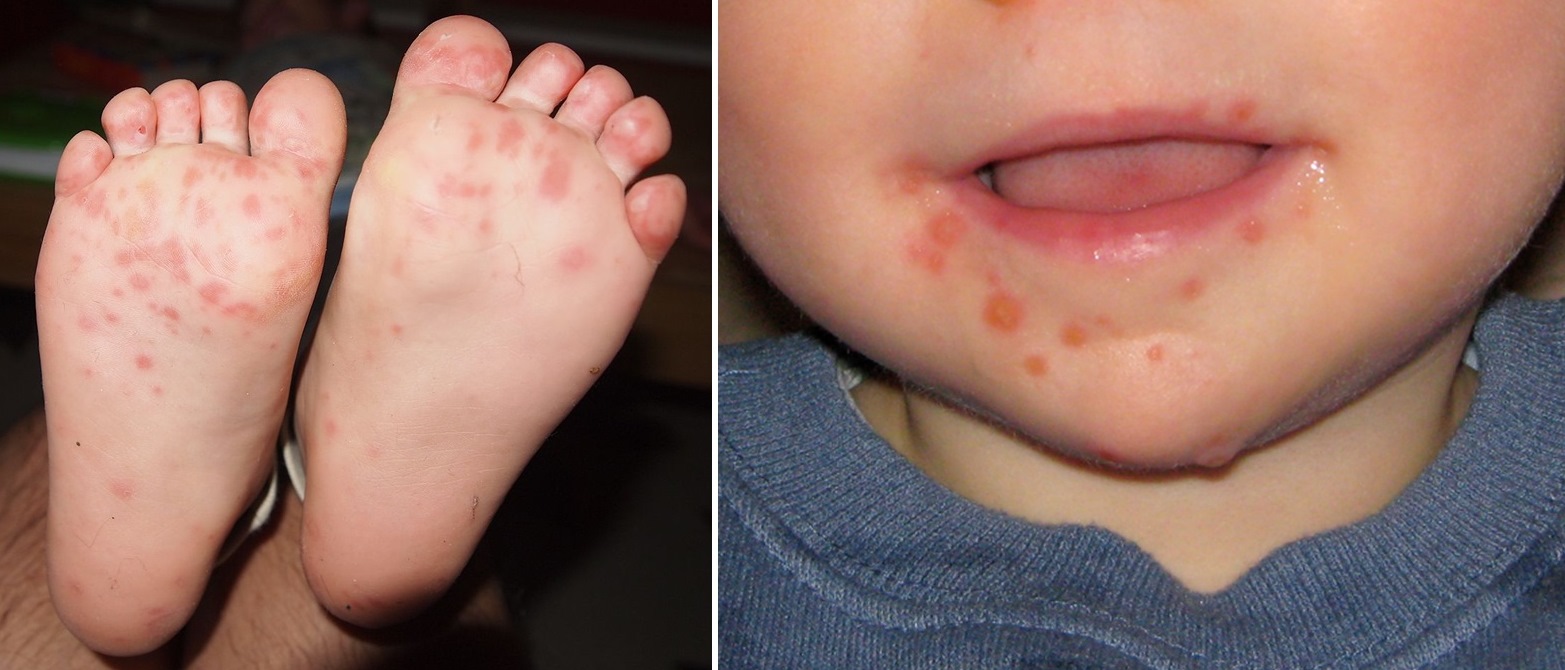
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common childhood illness caused by a virus. It is characterized by a fever, rash, and mouth ulcers.
The rash of HFMD typically appears on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. It can also spread to the arms, legs, and buttocks. The rash is usually red and bumpy, and it may blister. The mouth ulcers are typically small and round, and they can be painful. HFMD can also cause other symptoms, such as sore throat, runny nose, and loss of appetite.
Differential Diagnosis
HFMD can be difficult to distinguish from other similar conditions, such as chickenpox and measles. However, there are some key differences between these conditions. The rash of HFMD is typically more widespread than the rash of chickenpox, and the mouth ulcers of HFMD are typically more painful than the mouth ulcers of measles.
Laboratory Testing and Diagnostic Criteria
HFMD can be diagnosed based on the clinical symptoms. However, laboratory testing may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Laboratory testing can include viral culture, serology, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
- Viral culture is the most definitive test for HFMD. However, it can take several days to get results.
- Serology can be used to detect antibodies to the HFMD virus. However, serology is not as sensitive as viral culture.
- PCR is a rapid and sensitive test for HFMD. However, PCR is not as specific as viral culture.
The diagnosis of HFMD is typically made based on the clinical symptoms and the results of laboratory testing.
Management and Prevention: Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common viral infection that primarily affects young children. While it is generally a mild illness, it can cause discomfort and distress. Effective management and preventive measures are crucial to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and curb the spread of the virus.
General Principles of Treatment
Treatment for HFMD primarily involves supportive care and symptomatic management. Rest, adequate hydration, and pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate discomfort and fever. Maintaining good oral hygiene is also essential to prevent secondary infections in the mouth.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are not routinely recommended for HFMD as the infection typically resolves within a week. However, in severe cases, antiviral medications such as acyclovir or valacyclovir may be considered to reduce the duration and severity of symptoms.
Infection Control Measures
Preventing the spread of HFMD is crucial to control outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations. Effective infection control measures include:
- Frequent handwashing with soap and water or alcohol-based hand sanitizers
- Disinfecting frequently touched surfaces and objects
- Avoiding close contact with infected individuals
- Staying home from school or work if infected
- Proper disposal of used tissues and diapers